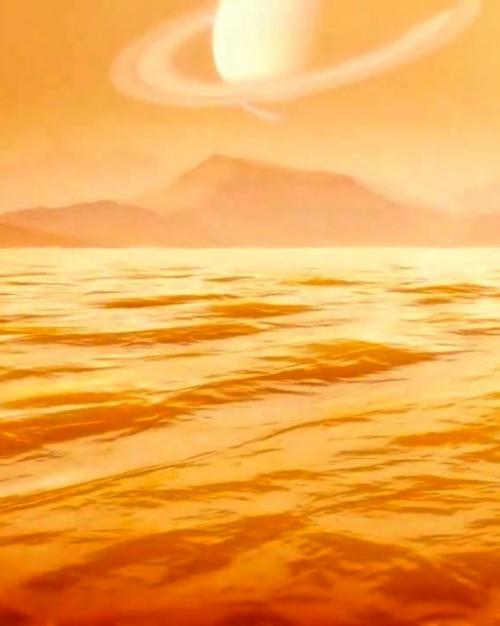
Far below the gaseous atmospheric shroud on Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, lies Kraken Mare, a sea of liquid methane. Cornell astronomers have estimated that sea to be at least 1,000 feet deep near its center – enough room for a potential robotic submarine to explore.
After sifting through data from one of the final Titan flybys of the Cassini mission, the researchers detailed their findings in “The Bathymetry of Moray Sinus at Titan’s Kraken Mare,” which published Dec. 4, 2020, in the Journal of Geophysical Research.
“The depth and composition of each of Titan’s seas had already been measured, except for Titan’s largest sea, Kraken Mare – which not only has a great name, but also contains about 80% of the moon’s surface liquids,” said lead author Valerio Poggiali, research associate in Cornell Center for Astrophysics and Planetary Science (CCAPS), in the College of Arts and Sciences.
A billion miles from Earth, frigid Titan is cloaked in a golden haze of gaseous nitrogen. But peeking through the clouds, the moonscape has an Earthlike appearance, with liquid methane rivers, lakes and seas, according to NASA.
In fact, the data for this discovery was gathered on Cassini’s T104 flyby of Titan on Aug. 21, 2014. The spacecraft’s radar surveyed Ligeia Mare – a smaller sea in the moon’s northern polar region – to look for the mysteriously disappearing and reappearing “Magic Island,” which was an earlier Cornell discovery.
While Cassini cruised at 13,000 mph nearly 600 miles above Titan’s surface, the spacecraft used its radar altimeter to measure the liquid depth at Kraken Mare and Moray Sinus, an estuary located at the sea’s northern end. The Cornell scientists, along with engineers from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, had figured out how to discern lake and sea bathymetry (depth) by noting the radar’s return time differences on the liquid surface and sea bottom, as well as the sea’s composition by acknowledging the amount of radar energy absorbed during transit through the liquid.
It turns out that Moray Sinus is about 280 feet deep, shallower than the depths of central Kraken Mare, which was too deep for the radar to measure. Surprisingly the liquid’s composition, primarily a mixture of ethane and methane, was methane-dominated and similar to the composition of nearby Ligeia Mare, Titan’s second-largest sea.
Earlier scientists had speculated that Kraken may be more ethane rich, both because of its size and extension to the moon’s lower latitudes. The observation that the liquid composition is not markedly different from the other northern seas is an important finding that will help in assessing models of Titan’s Earth-like hydrologic system.
Beyond deep, Kraken Mare also is immense – nearly the size of all five Great Lakes combined.
Titan represents a model environment of a possible atmosphere of early Earth, Poggiali said.
“In this context,” he said, “to understand the depth and composition of Kraken Mare and the Moray Sinus is important because this enables a more precise assessment on Titan’s methane hydrology. Still, we have to solve many mysteries.”
One such puzzle is the origin of the liquid methane. Titan’s solar light – about 100 times less intense than on Earth – constantly converts methane in the atmosphere into ethane; over roughly 10 million-year periods, this process would completely deplete Titan’s surface stores, according to Poggiali.
In the distant future, a submarine – likely without a mechanical engine – will visit and cruise Kraken Mare, Poggiali said.
“Thanks to our measurements,” he said, “scientists can now infer the density of the liquid with higher precision, and consequently better calibrate the sonar aboard the vessel and understand the sea’s directional flows.”
Co-authors on the paper are: Alex Hayes, professor of astronomy and director of CCAPS; Jonathan Lunine, the David C. Duncan Professor in the Physical Sciences, and chair, Department of Astronomy; Marco Mastrogiuseppe, former Cornell postdoctoral researcher, now research associate at Sapienza University of Rome, Italy; Alice Le Gall, The Institut Universitaire de France, Paris; and research associates Illeana Gomez-Leal and Daniel Lalich.
NASA provided funding for this research.
Read the story in the Cornell Chronicle.